

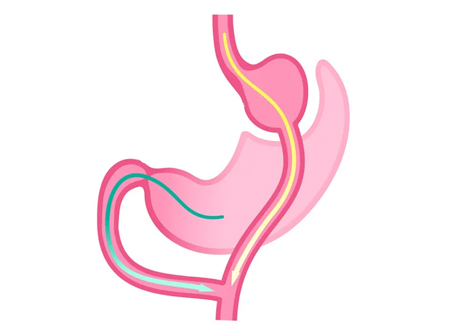
Biliopancreatic diversion
Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch Stapling is used to create a sleeve of the stomach retaining the natural stomach outlet. The majority of the small intestine is bypassed causing nearly complete malabsorption of food contents.
Advantages
- Recommended cure for high-level type 2 diabetes
- Weight loss result is greater than other procedures
- Provides the highest levels of malabsorption.
- A biliopancreatic diversion with a duodenal switch (BPD/DS) is a less common weight-loss procedure that entails two major steps.
The first step is sleeve gastrectomy in which about 70-80% of the stomach is removed, leaving a smaller tube-shaped stomach. However, the valve that releases food to the small intestine (the pyloric valve) remains, along with a limited portion of the small intestine that normally connects to the stomach (duodenum).
The second step bypasses the majority of the intestine by connecting the end portion of the small intestines to the duodenum near the stomach. A BPD/DS both limits how much you can eat and reduces the absorption of nutrients, including proteins and fats.
While a BPD/DS is very effective, it has more risks, including malnutrition and vitamin deficiencies. This procedure is generally recommended for people with a body mass index (BMI) greater than 60